Journal Name: Scholar Journal of Applied Sciences and Research
Article Type: Education
Received date: 27 March, 2019
Accepted date: 03 April, 2019
Published date: 10 April, 2019
Citation: Banihashemi SSA (2019) Future of Korean Peninsula from Aspect of Game Theory. Sch J Appl Sci Res Vol: 2, Issu: 5 (01-07).
Copyright: © 2019 Banihashemi SSA. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
Game theory is a scientific tool for prediction of future. In this article, in short, we explain basic information of game theory. we know that correct informatics need for game theory and if information’s are correct up to 90% prediction will be true. Now in the Korean peninsula everybody wants to know the future of USA and North Korea which with help of Game theory and software of Gambit and information’s which we collected show that what is future of Korean peninsula..
Keywords
Game theory, USA, North Korea, War, Strategies.
Abstract
Game theory is a scientific tool for prediction of future. In this article, in short, we explain basic information of game theory. we know that correct informatics need for game theory and if information’s are correct up to 90% prediction will be true. Now in the Korean peninsula everybody wants to know the future of USA and North Korea which with help of Game theory and software of Gambit and information’s which we collected show that what is future of Korean peninsula..
Keywords
Game theory, USA, North Korea, War, Strategies.
Introduction
A war policy that involves the regulation and implementation as well as the product and outcome of the leaders’ decisions is a guide for actions that a government runs beyond its borders in order to pursue its goals with respect to other government and non-state actors. The war largely focuses on the government’s view of how it deals with issues such as security, order, conflict, and cooperation, and is constantly evolving. On this basis, we will examine US policy and the future of these relations. we look through game theory, warlike and bullying policy of the United States In contrast to North Korea, and show that game theory It plays an essential role in politics, international relations and wars, and it is better to use game theory before starting any political negotiations and starting any relationship and war and always have a complete strategy for each action from its opponent.
America and North Korea War
America using zero-sum game in fear of North Korea’s ability and thinking on win and the loss for North Korea. The strategy and the process of the game are nothing but a defeat of the United States and North Korea’s increasing power in the region. That’s why it changed a bit in its North Korean game and tried to progress the game with a stacked amount [1]. The inexperienced foreign minister and his own strategies have come to pass, which is unlikely to result in loss or failure for Americans.
The Impact of Personality on Foreign Policy
What makes one’s foreign policy efficient is paying attention to the geopolitical position, economic status and internal affairs in terms of manpower, efficient and developed, and awareness of environmental contexts, especially in the international system [2].
Professor James Roznan believes that there are five variables that influence the foreign policy of the countries, which are among the most prominent theorists of international relations and the main determinants of US foreign policy, especially at the time of Ronald Reagan, and that these variables in the developed world have more power and influence [3]. And some like a personality variable in the Third World and developing countries have a greater degree of foreign policy formation. Ultimately, understanding the personality variable as the impact of individual and personality skills (mentally and intellectually) once again confirms Professor Rosen’s statement that in less developed or developing countries, foreign policy is heavily influenced by individuals and personality variables, unlike states It is developed that the variable of the structure and system has a higher position [4].
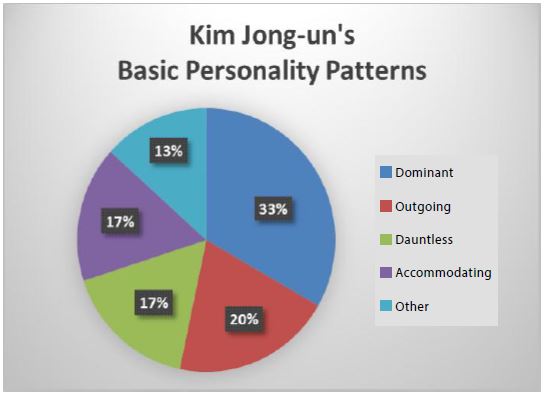
In this research, we have also psychologically examined both leaders for the sake of accuracy. Both characters are personally close to each other, both highly psycho and defeated in family and survivors’ lives. Both are selfish (Figures 1 and 2).
Therefore, both psychologically and psychologically, they are in the same position, and in conclusion, the prediction of the war in both is very high [5].
Figure 1:Kim Jong-un’s Basic Personality Patterns..
Figure 2:Donald Trump’s Basic Personality Patterns.
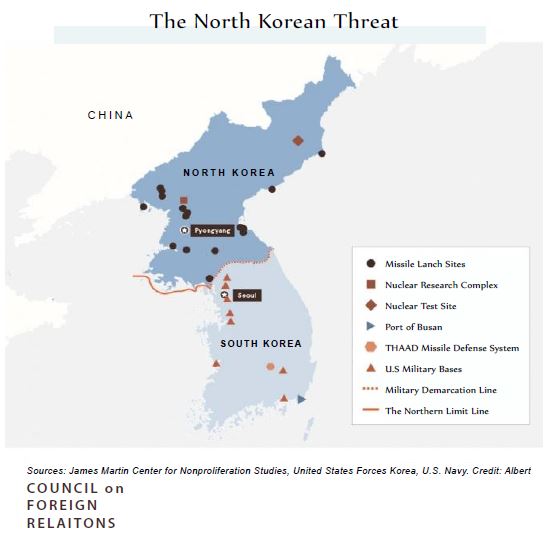
Although the United States currently has one of the strongest armies in the world, North Korea’s conditions are shown in Figure 3.
Half of the country’s income is spent on the military, and 50% of the people are in the army and military-affiliated factories, which is the fifth largest in the world. The proportion of the population to the army is an important point in the mood of the North Korean people, despite the difference in the strength of the spirit of warfare and their response is that we are ready to eat grass, but not under US coercion [6]. On the other hand, North Korea’s reach for US allies, including South Korea-Japan (Figure 4).
Economically, no doubt, the United States is one of the most powerful global economies, and in return, the Korean GDP is $ 1,800. With the tips mentioned and the information we get, we begin our mathematical model:
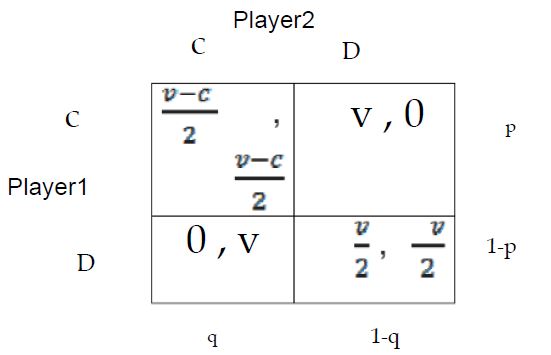
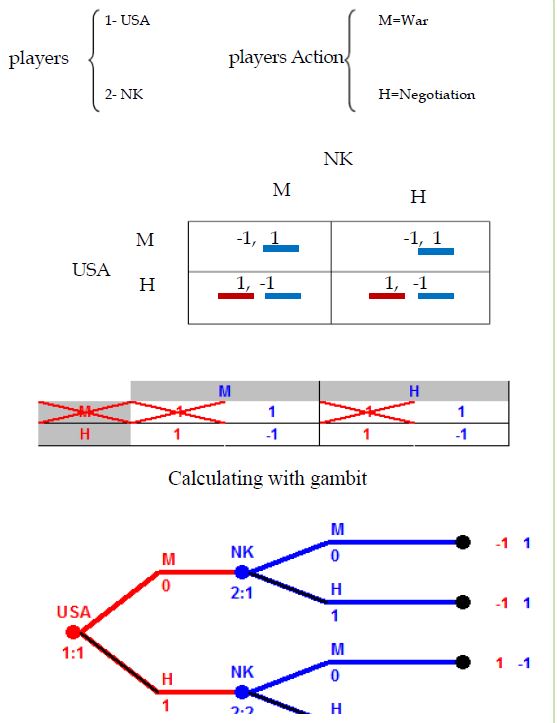
Showing strategic game as (Hawk-Dowe) (Figure 5).
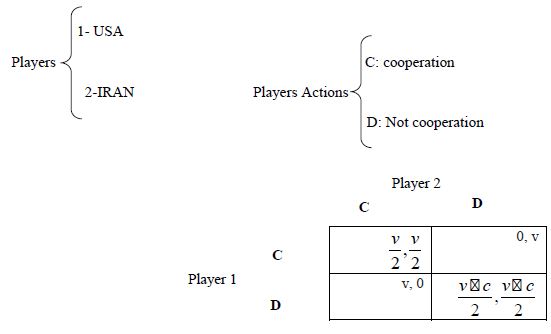
According to the game that the United States is taking, and North Korea is forced to continue, the net balance for the two countries is to cooperate, and the other does not cooperate [7]. This is the state’s desire for the United States, but since North Korea is planning to slow down the situation So, this is not the balance of the United States [8]. We suppose that it is probable that America will start a war, and what measures should be taken to prevent the United States from starting this war or negotiating with the North Koreans?.
Given the combination of equilibrium that occurred at (v/c, v/c)=(p,q) the probability of the US to start the war depends on the variables V and C (C>V). Assuming v2=C, the cost of war is twice the value of the source [9].
The probability of a war, and the greater the c is greater than v, the probability of a war will decrease, which is one of the ways to prevent this possible war (Figure 6).
Figure 3:North Korea’s Ballistic Missiles.
Figure 4:North Korean threat.
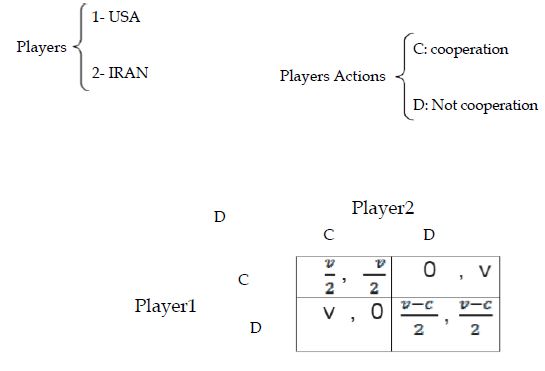
North Korea is interested in solving the problems of the region with the help of the United States to reach a peaceful area, but with regard to the strategies that the United States has taken, North Korea does not have enough confidence in the United States [10]. For this reason, North Korea prefers to play the puzzle of two prisoners with the United States in this game v>c.
Figure 7 shows the game to the strategic form (two prisoners puzzle).
The pure Nash equilibrium of the game is (D, D), meaning both countries can solve the crisis, while if the United States takes the correct strategy, it can solve the crisis without harming North Korea [11].
Regarding the conversations outside the praxis of Tramp and the subsequent North Korean leader, there is nothing but a hasty and unpredictable decision-making process to be prepared for any kind of behavior on their part. Therefore, North Korea needs to take steps to secure security [12]. Providing the country and expanding its power in any way. Assuming that Tramp talk against North Korea and North Korea’s threat to the war as a believable threat, North Korea must take the preparedness to deal with a possible war with
Figure 5:Strategic game as (Hawk-Dowe).
Figure 6:The probability of the US to start the war depends on the variables V and C.
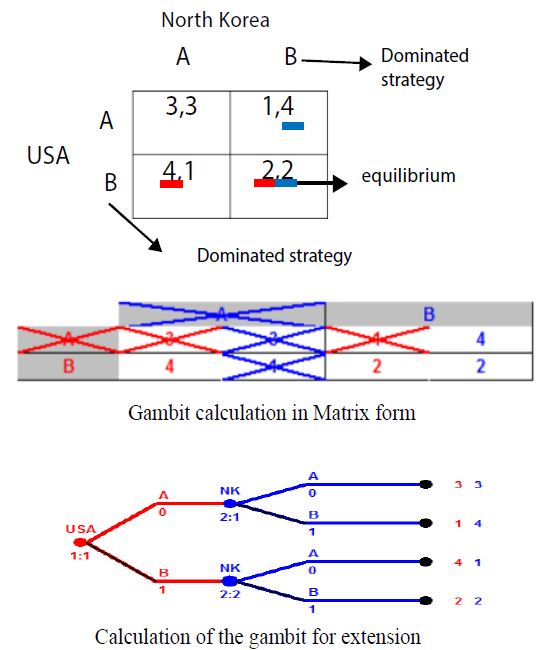
Figure 7:The game to the strategic form (two prisoners puzzle).
Figure 8:The application of the puzzle of two prisoners in international relations.
the United States. This readiness can be used to strengthen the military and the armed forces [13]. The game table is based on the application of the puzzle of two prisoners in international relations in the following form (Figure 8):
A=Preparation for war and increasing military and weaponry
B=Maintain existing forces and neglect to start a possible war
In the hope that there will be no war, the two countries cannot make any effort to increase their readiness, in which case there will not be a specific cost to the two sides, which is not the balance of the puzzle game in prison, which, according to Recent American behavior is not a good thing for North Korea [14]. If the two countries are struggling to increase the power of confrontation in the war, there will be plenty of costs, which, of course, will be lower for North Korea, but the United States will pay a great deal [15]. North Korea, due to its self-imposed sanctions and more weapons and military equipment. So, it’s better for North Korea to come up with a knowledge of the United States and it’s better to prepare for this possible battle, which will cost less in any case. As a result, they can increase their military capability in the region, with the exception of providing their own internal security with the task, very low possibility a country even thinks of attack North Korea [16-18].
America’s profit:
• American leadership in the world
• Increasing oil prices in favor of US allies
• Building a coalition against North Korea in practice against China and Russia
• Eliminating the North Korean resistance
• Attract maximum support from America and its Western allies
• Demonstrating the American, south korea, japan power in the neighborhood of the Russians and undermining their interests
• The isolation of China and Russia in Central Asia and eastern Asia
• An international consensus on North Korea and its performance in the region
• Attract support and support from Western backers
USA’s loss:
• Insecurity of the area
• Insecurity for the countries of the American allies in the region
• The growing power of the USA opposition
• The cost of weapons and the hiring of a large number for war
• Lowering the tourist
North Korea Profit:
• Show the main face of the United States of the world
• North Korea’s ability to be strong
• The possibility of a stronger anti-American front with North Korea, Russia and China
North Korea loss:
• Insecurity of the area
• Destroying the island of stability and tranquility in the region
• Increased arms costs rather than development costs
• lagging behind the scientific growth of the country
• becoming more dependent on countries like Russia and China and giving them more privilege
• The use of trans-national states such as France and the United States to strike North Korea
• North Korea’s strategic areas and facilities are blown away or destroyed
• Remaining sanctions and intensifying them
• popular discontent due to the prevention of a war or planning for it
Common benefit:
• Possibility to balance the power in the region
Common Loss:
• Insecurity in the in the region
• insecurity in oil and transportation
• the destruction of the assets of these two countries and spending a lot
• The effects of war on people in the country in terms of cultural, financial, scientific and livelihoods
• weakening of military, political and financial power in each country
• Abuse of countries and the rise in oil prices
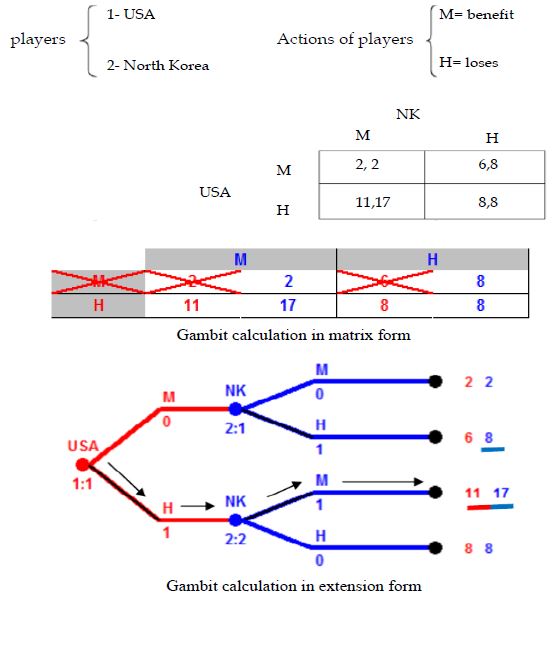
• The game shows that the best answer to this game is, in any event, the loss of North Korea due to the war (Figure 9).
American plan:
• American plan, kneeling North Korea.
• increase in oil prices
• weakening of military power and other financial region
• Eliminating the strength of resistance and thinking of resistance in the area
• North Korean rulers’ morale and character
• Americans adventure with North Korea intimidation and adventure for South Korea and Japan
Zero sum game:
North Korea is a peace-loving country, explaining that it will solve the problems through negotiation, and on the contrary, America is a warring country (according to the recent USA strategy), then if North Korea chooses a war, it will score points 1- and +1, If the North Korean choose negotiation, then +1 and America -1 [19,20]. Because the world is seeking peace and negotiating better than a war, then for war -1 and the negotiation +1 (Figure 10).
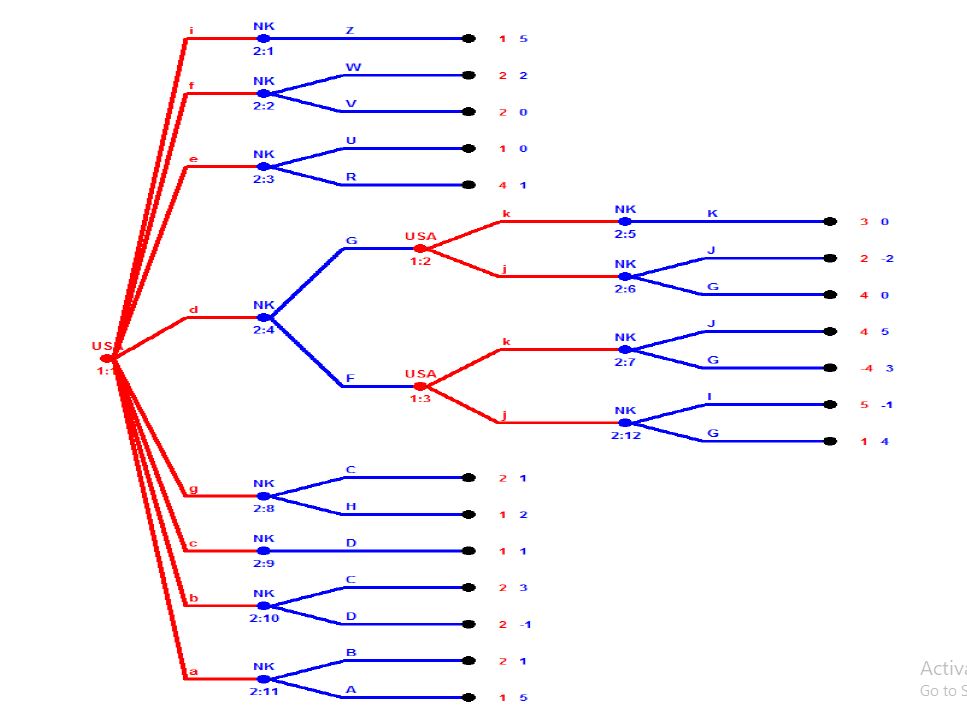
Game in extension form (Figure 11)
Players:
1) USA
2) NK
USA Actions
• Negotiations to resolve our issues between North Korea and the United States and relaxing relationships
• Divorce between people and Kim
• Increase the payload
• war with North Korea
• economic warfare
• trying to isolate North Korea with foreign partners
• Psychological warfare
• Nobody war
• Compromise
NK Actions
• acceptance of America’s conditions
• Dismissing US Terms
• neglect
Figure 9:The game shows that the best answer to this game is, in any event, the loss of North Korea due to the war.
Figure 10:Score points on the basis of war and negotiation.
Figure 11:Game in extension form.
• increased military weapons
• Define and neutralize
• Response to the USA-led war
• war
• neutralize the psychological warfare
• retreat
• compromise
• Economic Surrender
• non-economic surrender
• Isolated North Korea
• counteracting America
• Protecting the American people
• Nash equilibrium is equal to SPE={(dk,FJ)} under the full game play.
Given the numbers given to the measures taken and their comparison, they will be the path to decision-making for the United States and will have to fight against North Korea.
Trump D (2017) North Korea and the Risk of War Paul Rogers: Global Security Briefing.[ Ref ]
Abramowitz MI, Laney JT (2003) Meeting the North Korean Nuclear Challenge. Report of an Independent Task Force Sponsored by the Council on Foreign Relations.[ Ref ]
Albright D (2015) How much plutonium does North Korea have? Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists 50: 46-53.[ Ref ]
Albright D, Hinderstein C (2004) Verifiable, Irreversible, Cooperative Disarmament of the DPRK’s Nuclear Weapons Program. Presentation to the 45th Annual Meeting of the Institute for Nuclear Materials Management.[ Ref ]
Albright D, Holly H (2002) North Korea: It’s taking too long. Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists 58: 56-61.[ Ref ]
Albright D, O’Neill K (2000) Solving the North Korean Nuclear Puzzle. Washington, DC, Institute for Science and International Security Press.[ Ref ]
Bank of Korea (2004) Gross Domestic Product of North Korea in 2002. Press Release.[ Ref ]
Carpenter TG, Doug B (2004) The Korean Conundrum: America’s Troubled Relations with North and South Korea. New York, Palgrave Macmillan.[ Ref ]
Carter AB (2004) Implementing a Denuclearization Agreement with North Korea. Testimony before the Committee on Foreign Relations, US Senate.[ Ref ]
Cho SR (2009) The ROK-US Alliance and the Future of US Forces in South Korea. The Korean Journal of Defense Analysis 2: 77-104.[ Ref ]
Nicholas E (1999) The End of North Korea. Washington, DC, AEI Press.[ Ref ]
Nicholas E (2004) The Persistence of North Korea. Policy Review, No. 127.[ Ref ]
FAO/WFP Crop and Food Supply Assessment Mission to the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, December 22, 1995 and December 6, 1996.[ Ref ]
Paul K (2004) Deconstructed: North Korea’s Nuclear Program. Arms Control Today.[ Ref ]
Paul K (2004) Don’t Just Trust, Verify-Dismantling North Korea’s Nuclear Program. Arms Control Today.[ Ref ]
Moltz JC, Kenneth QC (2008) Getting Serious about a Multilateral Approach to North Korea.” The Nonproliferation Review 11: 136-144.[ Ref ]
Chang-hee N (2003) Relocating USFK Bases: Background and Implications. East Asian Review 15: 111-125.[ Ref ]
US Department of State (2003) Country Reports on Human Rights Practices, 2002: Democratic People’s Republic of Korea.[ Ref ]
US General Accounting Office (1999) Foreign Assistance: North Korea Restricts Food Aid Monitoring. Report to the Chairman, Committee on International Relations, House of Representatives, GAO/NSIAD-00-35.[ Ref ]
Wit JS, Poneman DB, Gallucci RL (2004) Going Critical. The First North Korean Nuclear Crisis. Washington, DC, Brookings Institute Press.[ Ref ]