Journal Name: Journal of Drug Development and Delivery
Article Type: Research
Received date: 09 January, 2019
Accepted date: 16 January, 2019
Published date: 23 January, 2019
Citation: Ahmed SH, Khasim SM, Babu RS, Shahnawaz J (2019) To Develop New RP-HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Estimation of Quinapril and Tolcapone in Pharmaceutical Dosage Form. J Drug Dev Del Vol: 2, Issu:1 (01-06).
Copyright: © 2019 Ahmed SH. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
A simple and selective LC method is described for the determination of Quinapril and Tolcapone. Chromatographic separation was achieved on a c18 column using mobile phase consisting of a mixture of 55 volumes of Water, 45 volumes of Methanol with detection of 220 nm. Linearity was observed in the range 2.5-7.5 μg /ml for Quinapril (r2 = 0.995) and 5-15 μg /ml for Tolcapone (r2 = 0.998) for the amount of drugs estimated by the proposed methods was in good agreement with the label claim.
The proposed methods were validated. The accuracy of the methods was assessed by recovery studies at three different levels. Recovery experiments indicated the absence of interference from commonly encountered pharmaceutical additives. The method was found to be precise as indicated by the repeatability analysis, showing % RSD less than 2. All statistical data proves validity of the methods and can be used for routine analysis of pharmaceutical dosage form.
Keywords
RP-HPLC, Quinapril, Tolcapone, Chromatographic separation.
Abstract
A simple and selective LC method is described for the determination of Quinapril and Tolcapone. Chromatographic separation was achieved on a c18 column using mobile phase consisting of a mixture of 55 volumes of Water, 45 volumes of Methanol with detection of 220 nm. Linearity was observed in the range 2.5-7.5 μg /ml for Quinapril (r2 = 0.995) and 5-15 μg /ml for Tolcapone (r2 = 0.998) for the amount of drugs estimated by the proposed methods was in good agreement with the label claim.
The proposed methods were validated. The accuracy of the methods was assessed by recovery studies at three different levels. Recovery experiments indicated the absence of interference from commonly encountered pharmaceutical additives. The method was found to be precise as indicated by the repeatability analysis, showing % RSD less than 2. All statistical data proves validity of the methods and can be used for routine analysis of pharmaceutical dosage form.
Keywords
RP-HPLC, Quinapril, Tolcapone, Chromatographic separation.
Introduction
Quinapril
Quinapril is a prodrug that belongs to the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor class of medications. It is metabolized to quinaprilat (quinapril diacid) following oral administration. Quinaprilat is a competitive inhibitor of ACE, the enzyme responsible for the conversion of angiotensin I (ATI) to angiotensin II (ATII). ATII regulates blood pressure and is a key component of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system (RAAS). Quinapril may be used to treat essential hypertension and congestive heart failure.
Mechanism of action: There are two isoforms of ACE: the somatic isoform, which exists as a glycoprotein comprised of a single polypeptide chain of 1277; and the testicular isoform, which has a lower molecular mass and is thought to play a role in sperm maturation and binding of sperm to the oviduct epithelium. Somatic ACE has two functionally active domains, N and C, which arise from tandem gene duplication. Although the two domains have high sequence similarity, they play distinct physiological roles. The C-domain is predominantly involved in blood pressure regulation while the N-domain plays a role in hematopoietic stem cell differentiation and proliferation. ACE inhibitors bind to and inhibit the activity of both domains, but have much greater affinity for and inhibitory activity against the C-domain. Quinaprilat, the principle active metabolite of quinapril, competes with ATI for binding to ACE and inhibits and enzymatic proteolysis of ATI to ATII. Decreasing ATII levels in the body decreases blood pressure by inhibiting the pressor effects of ATII as described in the Pharmacology section above. Quinaprilat also causes an increase in plasma renin activity likely due to a loss of feedback inhibition mediated by ATII on the release of renin and/or stimulation of reflex mechanisms via baroreceptors.
Tolcapone
Tolcapone is a drug that inhibits the enzyme catechol- O-methyl transferase (COMT). It is used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease as an adjunct to levodopa/carbidopa medication. It is a yellow, odorless, non-hygroscopic, crystalline compound. Tolcapone is associated with a risk of hepatotoxicity.
Mechanism of action: The precise mechanism of action of Tolcapone is unknown, but it is believed to be related to its ability to inhibit COMT and alter the plasma pharmacokinetics of levodopa, resulting in an increase in plasma levodopa concentrations. The inhibition of COMT also causes a reduction in circulating 3-OMD as a result of decreased peripheral metabolism of levodopa. This may lead to an increase distribution of levodopa into the CNS through the reduction of its competitive substrate, 3-OMD, for transport mechanisms. Sustained levodopa concentrations presumably result in more consistent dopaminergic stimulation, resulting in greater reduction in the manifestations of parkinsonian syndrome.
Aim and Objective
Aim
To develop new RP HPLC method for the simultaneous estimation of Quinapril and Tolcapone in pharmaceutical dosage form.
Objective
- Solubility determination of Quinapril and Tolcapone in various solvents and buffers.
- Determine the absorption maxima of both the drugs in UV–Visible region in different solvents/buffers and selecting the solvents for HPLC method development.
- Optimize the mobile phase and flow rates for proper resolution and retention times.
- Validate the developed method as per ICH guidelines.
Materials and Methods
Table 1 and 2
Table 1: Reagents used.
| Water | HPLC Grade |
|---|---|
| Methanol | HPLC Grade |
| Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate | AR Grade |
| Acetonitrile | HPLC Grade |
| Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate | AR Grade |
| Acetonitrile | HPLC Grade |
Table 2: Drugs used.
| QUINAPRIL AND TOLCAPONE drugs | Gift Samples obtained from Chandra labs, Hyd. |
|---|---|
| PFIZA (QUINAPRIL- 10mg & TOLCAPONE- 12.5) Tablet dosage form |
Obtained from local pharmacy |
Mobile phase
A mixture of 55 volumes of Water and 45 volumes of methanol were prepared. The mobile phase was sonicated for 10 min to remove gases.
Determination of working wavelength (λmax)
In simultaneous estimation of two drugs isobestic wavelength is used. Isobestic point is the wavelength where the molar absorptivity is the same for two substances that are interconvertible. So this wavelength is used in simultaneous estimation to estimate both drugs accurately.
Preparation of standard stock solution of Quinapril
10 mg of Quinapril was weighed and transferred in to 100ml volumetric flask and dissolved in methanol and then make up to the mark with methanol and prepare 10 μg/ml of solution by diluting 1ml to 10ml with methanol.
Preparation of standard stock solution of Tolcapone
10 mg of TOLCAPONE was weighed in to 100ml volumetric flask and dissolved in Methanol and then dilute up to the mark with methanol and prepare 10 μg/ml of solution by diluting 1ml to 10ml with methanol. Were soluble it was used as solvent for λ max determination by UV-Visible Spectroscopy.
Assay
Preparation of samples for assay
Preparation of mixed standard solution: Weigh accurately 10mg of Quinapril and 10 mg of Tolcapone in 100 ml of volumetric flask and dissolve in 10ml of mobile phase and make up the volume with mobile phase. From above stock solution 5 μg/ml of Quinapril and 10 μg/ml of Tolcapone is prepared by diluting 1.5ml to 10ml with mobile phase. This solution is used for recording chromatogram.
Sample preparation: 5 tablets (each tablet contains Tolcapone- mg, Quinapril- mg) were weighed and taken into a mortar and crushed to fine powder and uniformly mixed. Tablet stock solutions of Tolcapone and Quinapril (μg/ml) were prepared by dissolving weight equivalent to 10 mg of Tolcapone and 10mg of Quinapril and dissolved in sufficient mobile phase. After that filtered the solution using 0.45-micron syringe filter and Sonicated for 5 min and dilute to 10ml with mobile phase. Further dilutions are prepared in 5 replicates of 10 μg/ml of Tolcapone and 5 μg/ml of Quinaprilwas made by adding 1 ml of stock solution 1.5 to 10 ml of mobile phase.
Calculation: The amount of Tolcapone and Quinaprilpresent in the formulation by using the formula given below, and results shown in table 3.
Where,
AT = Peak area of sample preparation,
AS = Average Peak area of standard preparation,
WS = Weight of drug in mg,
DS & DT = Dilution of standard and sample preparation,
WT = Weight of Sample in Assay preparation,
P = Percentage purity of working standard,
LC = Label Claim of drug.
Table 3: Assay results.
| QUINAPRIL | TOLCAPONE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Area | Sample Area | Standard Area | Sample Area | |
| Injection-1 | 1136.114 | 1120.050 | 2576.974 | 2541.448 |
| Injection-2 | 1112.446 | 1121.051 | 2535.582 | 2551.500 |
| Injection-3 | 1115.176 | 1123.043 | 2549.337 | 2545.160 |
| Injection-4 | 1116.202 | 1118.821 | 2538.795 | 2551.600 |
| Injection-5 | 1124.282 | 1112.446 | 2544.742 | 2535.582 |
| Average Area | 1120.844 | 1118.942 | 2549.086 | 2545.058 |
| Standard deviation | 3.615683 | 6.83985 | ||
| %RSD | 0.323134 | 0.26875 | ||
| Assay(%purity) | 99.83032 | 99.84198 | ||
Observation
The amount of Quinapril and Tolcapone present in the taken dosage form was found to be 99.83% and 99.84% respectively.
Method validation
Validation: Validation is a process of establishing documented evidence, which provides a high degree of assurance that a specific activity will consistently produce a desired result or product meeting its predetermined specifications and quality characteristics. Method validation is the process of demonstrating that analytical procedures are suitable for their intended use and that they support the identity, quality, purity and potency of the drug substances and drug products.
Validation parameters
- a) Specificity / Selectivity
- b) Accuracy
- c) Precision
- d) Linearity & Range
- e) Limit of Detection
- f) Limit of Quantitation
- g) Robustness
- h) Ruggedness
- i) System Suitability
Results and Discussion
Wavelength Optimization by UV– SpectroscopyFigure 1
Figure 1
Figure 1: Wavelength optimization by UV– spectroscopy.
Method development and optimization of RP-HPLC method
Table 4
Table 4: Optimized chromatographic conditions.
| Mobile phase | Methanol:Water |
|---|---|
| Ph | - |
| Column | Inertsil ODS 3V column,C18(150x4.6 ID) 5µm |
| Flow rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Column temperature | Room temperature(20-25oC) |
| Sample temperature | Room temperature(20-25oC) |
| Wavelength | 220 |
| Injection volume | 20 µl |
| Run time | 6 min |
| Retention time | About 2.707 min for Quinapril and 3.953 min for Tolcapone. |
Method validation
System suitability: Standard solutions were prepared as per the test method and injected into the chromatographic system. The system suitability parameters like theoretical plates, resolution and asymmetric factor were evaluated.
Tables 5 and 6
Table 5: Results for system suitability of Quinapril.
| Injection | Retention time (min) | Peak area | Theoretical plates (TP) | Tailing factor (TF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.700 | 1136.114 | 2877 | 1.441 |
| 2 | 2.700 | 1112.446 | 2966 | 1.343 |
| 3 | 2.697 | 1115.176 | 2961 | 1.455 |
| 4 | 2.707 | 1116.202 | 2976 | 1.485 |
| 5 | 2.703 | 1124.282 | 2971 | 1.485 |
| Mean | 2.7014 | 1120.844 | - | - |
| SD | 0.003782 | 9.607 | - | - |
| %RSD | 0.139984 | 0.8574 | - | - |
Table 6: Results for system suitability of Tolcapone.
| Injection | Retention time (min) | Peak area | Theoretical plates | Tailing factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.947 | 2576.974 | 2476 | 1.500 |
| 2 | 3.937 | 2535.582 | 2554 | 1.477 |
| 3 | 3.933 | 2549.337 | 2550 | 1.512 |
| 4 | 3.953 | 2538.795 | 2576 | 1.477 |
| 5 | 3.947 | 2544.742 | 2567 | 1.512 |
| Mean | 3.9434 | 2549.086 | - | - |
| SD | 0.008173 | 16.46919 | - | - |
| %RSD | 0.207261 | 0.646082 | - | - |
Linearity
Tables 7,8 and 9
Figures 2 and 3
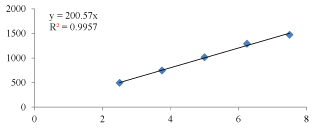
Figure 2: Linearity graph of Quinapril.
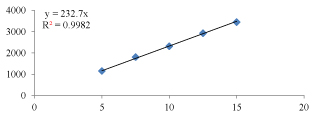
Figure 3: Linearity graph of Tolcapone.
Table 7: Linearity preparations.
| Preparations | Volume from standard stock transferred in ml | Volume made up in ml (with mobile phase) | Concentration of solution(µg /ml) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUINAPRIL | TOLCAPONE | |||
| Preparation 1 | 0.75 | 10 | 2.5 | 5 |
| Preparation 2 | 1.125 | 10 | 3.75 | 7.5 |
| Preparation 3 | 1.5 | 10 | 5 | 10 |
| Preparation 4 | 1.875 | 10 | 6.25 | 12.5 |
| Preparation 5 | 2.25 | 10 | 7.5 | 1.5 |
Table 8: Linearity of Quinapril.
| S.No. | Conc.(µg/ml ) | Area |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.5 | 495.227 |
| 2 | 3.75 | 745.541 |
| 3 | 5 | 1015.117 |
| 4 | 6.25 | 1290.46 |
| 5 | 7.5 | 1470.799 |
Table 9: Linearity of Tolcapone.
| S.No. | Conc.(µg/ml ) | Area |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 1152.124 |
| 2 | 7.5 | 1807.304 |
| 3 | 10 | 2315.072 |
| 4 | 12.5 | 2929.514 |
| 5 | 15 | 3454.098 |
Observation: The correlation coefficient for linear curve obtained between concentration vs. Area for standard preparations of Quinapril and Tolcapone is 0.995 and 0.998.
Recovery
Tables 10 and 11
Table 10: Recovery results for Quinapril.
| Recovery level | Accuracy Quinapril | Average % Recovery | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount taken(mcg/ml) | Area | Average area | %Recovery | ||
| 50% | 2.5 | 1147.472 | 1142.193 | 101.985 | 101.54 |
| 2.5 | 1147.472 | ||||
| 2.5 | 1131.636 | ||||
| 100% | 5 | 1282.181 | 1287.862 | 103.48 | |
| 5 | 1290.460 | ||||
| 5 | 1290.945 | ||||
| 150% | 7.5 | 1391.221 | 1388.523 | 99.18 | |
| 7.5 | 1373.610 | ||||
| 7.5 | 1400.738 | ||||
Table 11: Recovery results for Tolcapone.
| Recovery level | Accuracy Tolcapone | Average % Recovery | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount taken(mcg/ml) | Area | Average area | %Recovery | ||
| 50% | 5 | 2581.774 | 2573.486 | 102.06 | 102.81 |
| 5 | 2581.774 | ||||
| 5 | 2556.911 | ||||
| 100% | 10 | 2933.859 | 2948.693 | 105.45 | |
| 10 | 2936.438 | ||||
| 10 | 2975.781 | ||||
| 150% | 15 | 3186.091 | 3175.224 | 100.94 | |
| 15 | 3146.856 | ||||
| 15 | 3192.726 | ||||
Observation: The percentage mean recovery of Quinapril and Tolcapone is 101.54% and 102.81% respectively.
Precision
Table 12
Table 12: Method precision results for Quinapril and Tolcapone.
| Quinapril | ||
|---|---|---|
| S.No. | Rt | Area |
| 1 | 2.660 | 1109.066 |
| 2 | 2.667 | 1110.202 |
| 3 | 2.680 | 1113.271 |
| 4 | 2.683 | 1112.450 |
| 5 | 2.680 | 1108.599 |
| 6 | 2.690 | 1109.570 |
| Avg | 2.676667 | 1110.526 |
| stdev | 0.011057 | 0.1564 |
| %RSD | 0.412278 | 0.3421 |
| Tolcapone | ||
|---|---|---|
| S.No. | Rt | Area |
| 1 | 3.890 | 2518.891 |
| 2 | 3.900 | 2515.559 |
| 3 | 3.917 | 2514.373 |
| 4 | 3.903 | 2512.866 |
| 5 | 3.913 | 2517.609 |
| 6 | 3.923 | 2519.468 |
| avg | 3.907667 | 2516.461 |
| stdev | 0.012193 | 0.4321 |
| %RSD | 0.311401 | 0.2653 |
Observation: Test results for Tolcapone and Quinapril are showing that the %RSD of Assay results are within limits. The results were shown in table 12.
Limit of detection
Where, σ = the standard deviation of the response
S = the slope of the calibration curve
The slope S may be estimated from the calibration curve
of the analyte.
LOD of Quinapril = 0.79 μg/ml
LOD of Tolcapone = Tolcapone
Observation: The LOD for this method was found to be 0.79 μg/ml Quinapril and 2.95 μg/ml for Tolcapone
Limit of quantification
Where,
σ = the standard deviation of the response
S = the slope of the calibration curve
The slope S may be estimated from the calibration curve
of the analyte.
LOQ of Quinapril = 0.98μg/ml
LOQ of Tolcapone = 3.79 μg/ml
Observation: The LOQ for this method was found to be 0.98μg/ml for Quinapril and 3.79 μg/ml for Tolcapone.
Robustness
Table 13
Table 13: Robustness.
| Parameter | Quinapril | Tolcapone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retention time(min) | Tailing factor | Retention time(min) | Tailing factor | |
| Flow Rate 0.8 ml/min 1.2 ml/min |
3.727 2.127 |
1.558 1.464 |
5.457 3.113 |
1.589 1.421 |
| Wavelength 218nm 222nm |
2.707 2.657 |
1.412 1.382 |
3.960 3.903 |
1.500 1.477 |
Observation: From the observation it was found that the system suitability parameters were within limit at all variable conditions.
Ruggedness
Observation: From the observation the between two analysts Assay values not greater than 2.0%, hence the method was rugged.
Table 14
Table 14: Ruggedness.
| Quinapril | %Assay | Tolcapone | %Assay |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analyst 01 | 99.516 | Analyst 01 | 100.144 |
| Anaylst 02 | 99.38 | Anaylst 02 | 100.461 |
Discussion
A simple and selective LC method is described for the determination of Quinapril and Tolcapone in tablet dosage forms. Chromatographic separation was achieved on a c18 column using mobile phase consisting of a mixture of 55 volumes of water and 45 volumes of Methanol with detection of 220 nm. Linearity was observed in the range 2.5-7.5 μg/ml for Quinapril (r2 = 0.995) and 5-15 μg /ml for Tolcapone (r2 = 0.998) for the amount of drugs estimated by the proposed methods was in good agreement with the label claim.
The proposed methods were validated. The accuracy of the methods was assessed by recovery studies at three different levels. Recovery experiments indicated the absence of interference from commonly encountered pharmaceutical additives. The method was found to be precise as indicated by the repeatability analysis, showing %RSD less than 2. All statistical data proves validity of the methods and can be used for routine analysis of pharmaceutical dosage form.
Conclusion
From the above experimental results and parameters it was concluded that, this newly developed method for the simultaneous estimation Quinapril and Tolcapone was found to be simple, precise, accurate and high resolution and shorter retention time makes this method more acceptable and cost effective and it can be effectively applied for routine analysis in research institutions, quality control department in meant in industries, approved testing laboratories studies in near future.
There are no references