Journal Name: Journal of Psychology and Psychiatry Studies
Article Type: Research
Received date: 27 May, 2019
Accepted date: 17 June, 2019
Published date: 24 June, 2019
Citation: Pardede JA (2019) The Effects Acceptance and Commitment Therapy and Health Education Adherence to Symptoms, Ability to Accept and Commit to Treatment and Compliance in Hallucinations Clients Mental Hospital of Medan, North Sumatra. J Psychol Psychiatry Stud Vol: 1, Issu: 1 (30-35).
Copyright: © 2019 Pardede JA. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
Background: Schizophrenia nursing problems most commonly found is hallucinations. Found 55% of client hallucinations who have a relapse and medication adherence. This study aims to obtain the effects Acceptance and Commitment Therapy and Health Education adherence to symptoms, ability to accept and commit to treatment and compliance in Hallucinations clients Mental Hospital of Medan, North Sumatra.
Method: This research design quasi-experimental pre-test post-test with control group. This sampling technique was purposive sampling, where the sample is 90 clients with schizophrenia, 30 the intervention group were given Acceptance and Commitment Therapy and medication adherence health education, intervention group were given 30 Acceptance and Commitment Therapy and 30 control group.
Result: Results of this study found a reduction in symptoms hallucinations increased ability to accept and commit to the treatment of schizophrenia and compliance client who gets Acceptance and Commitment Therapy and health education medication adherence was significantly greater than the group that only get Acceptance and commitment Therapy (p<0.05).
Conclusion: Acceptance and commitment therapy and medication adherence health education recommended as a therapeutic nursing and therapy support advanced nursing care for clients in the risk of schizophrenia with hallucinations.
Keywords
Acceptance and Commitment therapy, Health Education medication adherence, Hallucinatios.
Abstract
Background: Schizophrenia nursing problems most commonly found is hallucinations. Found 55% of client hallucinations who have a relapse and medication adherence. This study aims to obtain the effects Acceptance and Commitment Therapy and Health Education adherence to symptoms, ability to accept and commit to treatment and compliance in Hallucinations clients Mental Hospital of Medan, North Sumatra.
Method: This research design quasi-experimental pre-test post-test with control group. This sampling technique was purposive sampling, where the sample is 90 clients with schizophrenia, 30 the intervention group were given Acceptance and Commitment Therapy and medication adherence health education, intervention group were given 30 Acceptance and Commitment Therapy and 30 control group.
Result: Results of this study found a reduction in symptoms hallucinations increased ability to accept and commit to the treatment of schizophrenia and compliance client who gets Acceptance and Commitment Therapy and health education medication adherence was significantly greater than the group that only get Acceptance and commitment Therapy (p<0.05).
Conclusion: Acceptance and commitment therapy and medication adherence health education recommended as a therapeutic nursing and therapy support advanced nursing care for clients in the risk of schizophrenia with hallucinations.
Keywords
Acceptance and Commitment therapy, Health Education medication adherence, Hallucinatios.
Introduction
Schizophrenia is a group of psychotic reaction that affects a wide range of individual function areas, including think, communicate, receive, interpret reality, feel and show emotion [1]. According [2] defines that schizophrenia i.e. chronic disease, severe and disabling brain disorder, which is characterized by chaotic mind, delusion, hallucinations, and bizarre behavior. Schizophrenia prevalence estimated at 1.5% 0.2% equally decreased for men and women in all age levels [3].
National Advisory Mental Health Council, 2001; The National Institute Of Mental Health, 2008 in [4], said the 2-4 million people, or 1.1% of the population on Earth suffering from schizophrenia or a disorder similar to schizophrenia are destructive to self-awareness for many individuals but they do not realize that they are sick and need treatment. Statistics show that about 40% of inhabitants (1.0 million) did not receive the psychiatric care led to homelessness, incarceration or violence.
Client experienced a 70% of schizophrenia hallucinations [5]. Hallucination is a State of a person experiencing a change in the pattern and amount of stimulation that are initiated internally or externally the vicinity with subtraction, exaggeration, distortion, or abnormalities of be respond against each stimulus [6]. It is also supported by [7] stating the hallucinations of schizophrenia symptoms are hearing is the most frequently encountered of the 50%-80% of the whole hallucination. Hallucinations can be a reason why clients doing violent behavior because sound - a sound that gave him a command so that the vulnerable do not adaptive behavior. Violent behavior is a response to maladaptive of anger, the result of extreme anger or panic. Violent behavior that occurs on the client is started by the presence of schizophrenia feelings of worthlessness, fear and rejected by the environment so that individuals will step aside from interpersonal relations with others [5].
Clients of schizophrenia often suffer recurrences because recurrence is the State of the disease after being in recovery period caused three factors, namely: the drug aspect, the aspect of patient and family aspects [8]. The client stopped the treatment because the treatment has not been felt necessary. Failure and disobedience in the drinking cure according the program is the reason most often in the recurrence of schizophrenia and re-entered the hospital. The causes of schizophrenia are not regular clients of drinking cure is due to interruption of reality and the inability to take a decision and a long hospitalization give the consequences of the decline of the mark on the client with the loss of motivation and responsibility, apathy, avoid activities and social relationships, basic capabilities are often compromised, such as independent living activities and treatments a day [8]. So that, the comprehensive nursing actions is needed to handle clients of schizophrenia.
Some research has been done to decrease the symptoms of violent behavior. Granting Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT) on clients of schizophrenia with violent behavior may increase cognitive ability and behavior of clients [9]. The results of other studies showed a difference in decreasing signs and symptoms of a client’s violent behavior after being given meaningful CBT and Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) [10]. Research using Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is very effective in creating acceptance, attention and more open in developing the capabilities of the client of schizophrenia [11]. by decreasing the angry and violent behavior symptoms [12] and [13], social, affective symptoms and improves hallucinations that occur on a client’s schizophrenia [3]. The results of research conducted by [14] obtained results that CBT can improve the cognitive ability of 29.31% and 22.4% of behavior capabilities on the client of schizophrenia with low selfesteem [16] found a decrease in symptoms and an increased ability of client’s low self-esteem who got CBT and REBT is larger than not getting CBT and REBT (p < 0.05). Some of the research done indicates that by using nursing therapy were able to cope with schizophrenia with the risk of violent behavior, hallucinations, and low self-esteem especially with using Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
Table 1: The relationship of ability to receive and committed in the treatment with Hallucinatory Schizophrenia Clients.
| Variable | r | P |
|---|---|---|
| The ability to receive and Committed Treatment *hallucinations symptoms | 0.489 | 0.000 |
There is a moderate relationship (r = 0.489) between the ability accept and committed to a treatment with a decrease in symptoms of hallucination. The results of statistical tests is obtained there is a significant (p=α < 0.05).
Based on the results of some research indicates nursing actions proven specialists able to handle clients of schizophrenia as already described above, but needs to be anticipated to avoid recurrence due to disobedience so that taking the drug therapy of nursing health education need to be combined with medication compliance. Health education compliance taking medication is the giving of information to the patient in order to affect the patients dutifully drank a drug so that it does not cause recurrence and not returns home sick for hospitalization. According to [16] said that compliance with medication in people with an open behavior (overt Behaviour). Therefore, it could be said compliance with medication (medication compliance) are consuming the doctor prescribed drugs at the right dose and time since treatment will only be effective if the sufferer complies with rules in the use of the drug. The drug regularly and in accordance with the dosage, the client was able to recover from his illness coupled with specialist nursing and therapy health education that cognitive and behavioral change client so obediently drank the medicine.
Methods
The research design used in this research is the “Quasi experiment Pre-Post Test with Control Group” by giving health education ACT and taking medication compliance in the intervention group 1, only ACT in the intervention group 2. Clients who made the samples is a client who experiences hallucinations in Area of Medan Province of North Sumatra which meet the criteria of this research including: diagnose client schizophrenia, schizophrenia aged 18-60 years, clients a schizophrenia relapse/relaps ≥ 1, the client enters hospital for violent behavior (rage, rampage, injuring yourself , other people or the environment), the diagnosis of nursing the schizophrenia clients, hallucination and are already getting therapy nursing generalists, the client is obliged at the screening to find out therapeutic action of generalist, quiet or not clients in the behavior of running amok, the client can read and write, and clients are willing to be respondents and following therapy and health education was given.
The sampling techniques used in this research with technical purposive sampling with a total sample of 90 respondents, 30 reponden that get the ACT and health education taking the drug (intervention), 30 respondents who received ACT (interventions 2) as well as 30 control group.
The intervention group 1, group 2 and control the same intervention-the same get therapy generalist in accordance with standards applicable in hospitals, and to the intervention group was given also the ACT of each session during the 30- 45 minutes. On session 1: the client is guided to identify adverse events and reveals the thoughts, feelings and Behaviour a arising out of the incident. Session 2: identifying and selecting the value of her life based on experiences so that it can help resolve the problem of Client facing and revamp the wrong mindset to become true. Session 3: client practice received a Genesis based on a value selected or the client who taught clarify values and capabilities. Session 4: a commitment to client value is selected to modify behavior to prevent recurrence. The intervention group also get health education compliance medication consisting of 2 sessions each for 25 – 30 minutes includes: session 1: describe the management of treatment for schizophrenia patients with the risk of violent behavior, hallucinations and low selfesteem and session 2: goal setting and form a plan of action.
The measurement of symptoms hallucinations on each client is done at the beginning. The Research was conducted by modified Launed Slade Hallucination Scale. So too for the measurement of the ability to receive and committed to treatment using Acceptance and Action Questionnaire [11] and Compliance measurement using Medication Adherence Rating Scale for the (psychoses MARS; [17] measurements of hallucinations using LSHS consists of 12 items which measures the response of cognitive, affective, psychomotor, and social. On the measurement of observation consisted of 15 items that measure physical responses. Measurement capabilities received and committed to treatment using a modification of the Acceptance and Action Questionnaire [11] which consisted of 16 items and taking medication compliance measurements using a modification of Medication Adherence Rating Scale for the psychoses MARS; [17] which consists of 20 items. Analysis of symptoms, the ability to receive and committed to the treatment and compliance is done by using the paired t test, Anova test and correlation test.
Results
The results of this study indicate the age range of clients on average 35 years old between 19 years to 58 years, has maintained average frequency 3 times the most banyak12 time and at least 2 times, male-sex as many as 47 people and 43 women, highly educated as much as 46 people and 44 low educated people, clients who work as many as 70 people and it does not work as many as 20 people , married as many as 40 people and 50 people who were not married/divorced and have a history of disturbances of the soul as much as 79 people and does not have a history of disturbances of the soul as much as 11 people. Test results showed variable equality of education, occupation, and marital status are equivalent (p>0.05), while for the variable gender, psychiatric history and are not equivalent (p < 0.05).
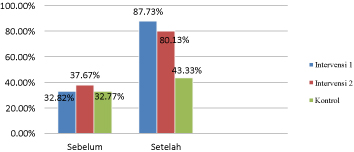
Figure 1 shows symptoms of hallucinations in the intervention group 1 before the education ACT and given medication compliance of 01 (84%), intervention 2 before the given ACT of 19.97 (37.67%) and control group of 23 (32.77%). Symptoms of hallucinations in the intervention group 1 after the education ACT and given medication compliance of 46 (113.95%), intervention 2 after the given ACT of 80.13 (42.47%) and group control of 24.30 (43.33%). A statistics test results showed no difference in meaning between the intervention group and the control group 1, after granting two therapy interventions (p-value < 0.05). Change of hallucinations in the intervention group 1 of the education ACT and given medication compliance of 29.10 (54.9%), intervention 2 given ACT of 22.50 (64.05%) and group control of 2.83 (18%) (Figure 1).
Figure 1:
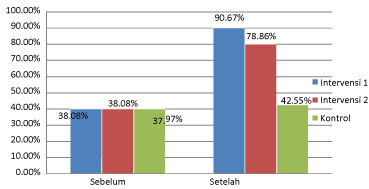
Figure 2 shows the ability to receive and committed on the treatment in the intervention group 1 before given the education ACT and compliance with medication of 24.37 (38.08%), 2 intervention before the given ACT of 24.37 (38.08%) and a control group of 24.30 (37.97%). The results of the statistical tests show there is equality (p. > 0.05). The ability to receive and committed on the treatment in the intervention group 1 after the education ACT and given medication compliance of 58.03 (90.5%), given the ACT 2 after intervention of 50.47 (78,86%) and a control group of 27.23 (42.55%). The results of statistical tests showed no difference in meaning between the intervention group 1, group 2 and control intervention after the giving of the therapy (p < 0.05). Changes in the ability to receive and committed in the treatment group 1 intervention given the education ACT and compliance with medication of 33.68 (52.71%), intervention 2 given ACT of 26.10 (40.78%) and a control group of 2.93 (4.58%) (Figure 2).
Figure 2:
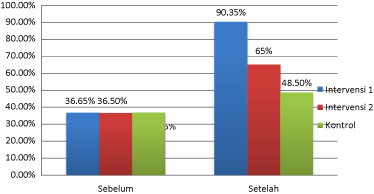
Figure 3 shows adherence to the intervention group 1 before the ACT and given medication compliance of education of 7.33 (36.65%), 2 intervention before the given ACT amounted to 7.30 (36.50%) and a control group of 7.37 (36.85%). The results of the statistical tests show there is equivalence (p-value > 0.05) compliance in the intervention group 1 after the education ACT and given medication compliance of 18 (80.28%), given the ACT 2 after intervention of 13.00 (65%) and a control group of 9.70 (48.5%). The results of statistical tests showed no difference in meaning between the intervention group 1, group 2 and control intervention after the giving of the therapy (p-value < 0.05). Changes of compliance in the intervention group 1 given the education ACT and compliance with medication of 10.73 (33.4%), intervention 2 given ACT of 5.70 (28.5%) and a control group of 2.33 (11.65%) (Figure 3).
Figure 3:
Discussion
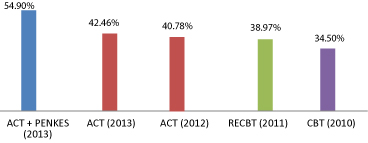
Nursing therapy given proved to be able to decrease the symptoms of hallucinations as already conducted in some other researches, as shown in figure 4.
Figure 4:
Hayes asserts that the ACT good clients for not avoiding the purpose of his life or able to accept his life and committed against him so that it is able to solve the problem [11]. This is supported by Stuart who said that clients should be able to get by with what is already chosen when it was committed. So by being able to accept and commit the client expected will not experience recurrence again. The hope nursing therapy as the ACT needs to be given to some clients so that it is able to decrease the symptoms of the disease, as can be seen the ACT coupled with health education’s compliance with medication were able to decrease the symptoms well. Research gaining increasing after a given health education ACT and compliance with medication, where an increase in the average score means prove decline symptoms in schizophrenia respondents with low self-esteem.
Decrease symptoms of low self-esteem in 1 intervention group of respondents 41.63% consists of cognitive symptoms decrease of 40.97%, 39.15% of affective, psychomotor of 38.93%, amounting to 45.47%, social and physical of 32.8%. In the intervention group 2 which just getting the ACT alone of 24.51% found a decrease amount in cognitive symptoms of 22.5%, 24.4% of affective, psychomotor of 22.86%, 25.75% of social, physical and amounted to 32.6%. While the group that did not get therapy also experienced a decrease in symptoms of 7.74% consisting of cognitive response of 9.32%, amounted to 1.42% affective, psychomotor of 5.72%, amounting to 30% of the social and physical of 24.8%.
Conclusion
Symptoms the risk of violent behavior on the client who gets schizophrenia ACT and health education compliance significantly decreased medication of 43.71%, clients of schizophrenia that get meaningful decreases of ACT 36.85% and not getting the therapy decline meaningfully of 5.94%. Symptoms of hallucinations in the client schizophrenia are getting health education ACT and compliance with medication decreases meaning of 54.9%, clients of schizophrenia that get significantly decreased ACT of 64.05% and not getting the therapy significantly decreases of 10%. Symptoms of low self-esteem on the client schizophrenia are getting health education ACT and compliance with medication decreased meaning of 41.63%, clients of schizophrenia that get significantly decreased ACT of 24.51% and not getting the therapy significantly decreases of 7.74%. The ability to receive and committed to client treatment schizophrenia after being given health education ACT and compliance with medication is increased significantly of 52.71%, the ability to receive and committed to client treatment of schizophrenia after a given ACT significantly increase of 40.78%, while the ability to receive and committed to client treatment of schizophrenia are not getting therapy significantly increases amounting to 4.58%. Client compliance of schizophrenia after a given health education ACT and compliance with medication significantly increases of 33.4%, the client’s compliance of schizophrenia after a given ACT significantly increase of 28.5%, while the client’s compliance of schizophrenia is not getting the therapy increased means of 11.65%.
Results of the study prove that ACT which is given on the client can accept improve schizophrenia and committed to the treatment and also health education can improve medication compliance clients to take drugs as well as both capable of lowering the risk of symptoms of violent behavior, hallucinations and low self-esteem clients schizophrenia so it can be applied as a therapy specialist in the hospital or in the community. The results of this research can be used as evidence based in comparing the influence of several therapies that can be rendered on the client or clients with schizophrenia diagnosis and research need to be developed by combining ACT with FPE because clients need a support system of family as the giver of moral or material so that the client is willing to accept and committed to treatment. In addition to FPE, the ACT can also be combined with the Logo of therapy, PMR, and other health education as well as compliance with medication also needs to be combined with BT, CBT, REBT, RECBT, and another therapy so that the client is being treated want to dutifully taking the drug, which means it is one of the recommended therapy need compliance health education combined with medication.
There are no references